Types of Eye Trauma & Emergencies
Corneal Abrasions
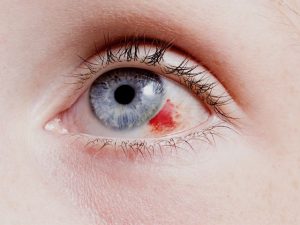
Any disruption of the corneal epithelium via foreign bodies or trauma can cause significant discomfort, photophobia, erythema, excessive lacrimation, and decreased visual acuity. For providers, fluorescein staining is the most useful clinical tool when assessing the injury.
Fluorescein dye adheres to the abrasion and fluoresces under cobalt blue light. Discharge instructions include topical antibiotics and daily follow-up. For patients with simple corneal abrasions, tetanus prophylaxis is unnecessary unless the trauma to the eye is penetrating.
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
Patients who experience sudden loss of eyesight in one eye need emergent screening for central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO). The abrupt blockage of the central artery can cause hypoperfusion of the retinal artery, progressing to cellular damage, and vision loss.
To avoid irreversible retinal damage and blindness, treatment relies on the identification of embolus (cholesterol, calcium, and platelet-fibrin) or thrombus (atherosclerotic disease, collagen-vascular disease, inflammatory states, and hypercoagulable). Individuals with the comorbidities of high blood pressure, glaucoma, or diabetes are at a higher risk of arterial blockage.
Risk factors include:
- being male
- hypertension
- smoking
- hyperlipidemia
- diabetes
- hypercoagulable state
Retinal Detachment
New floaters, flashes of light, dark shadow, or curtain in one eye or both eyes require emergent consideration for retinal detachment. A detached retina is a serious ocular condition and medical emergency that can lead to permanent vision loss.
If the retina detaches, it loses its oxygen and nutrients, leading to the death of the tissue. In the emergency setting, prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to avoid morbidity. Diagnosis requires a dilated eye exam.
Open Globe
When treating patients with eye trauma, evaluation of globe integrity is paramount for the potential vision-threatening emergency. In trauma, globe rupture describes open globe injuries, globe lacerations and globe perforation. Disruption of the globe can occur via penetration, perforation, laceration, or rupture due to blunt force trauma.
Workplace injuries, assaults, gunshots, sporting injuries, stab wounds, blast wounds, and motor vehicle accidents are the common causes of globe trauma and in the elderly, ground-level falls.
For diagnosis, clinical ophthalmologic examination comprises a slit lamp and fundoscopic exam. Recommendations include stat ophthalmologic consultation.